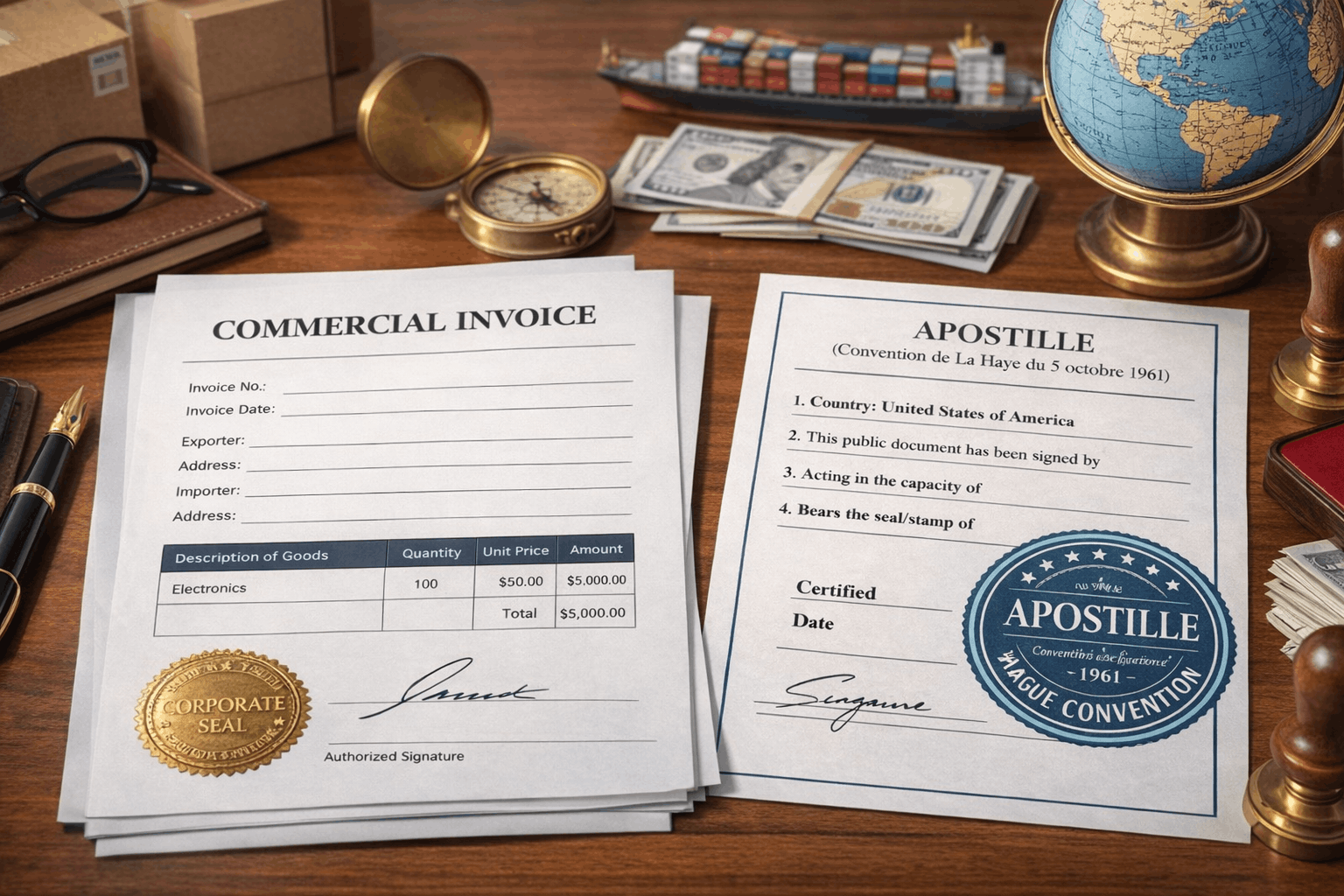
Commercial Invoice Apostille for International Trade: Step-by-Step Guide
Commercial invoices serve as passports for your goods in today’s fast-paced global marketplace. Foreign authorities require these documents to be authenticated before they can cross borders, making apostille services for commercial invoices indispensable to safeguard seamless market entry.
Whether requesting payments or shipping goods, understanding how to authenticate your critical trade documents allows you to save time and keep your global transactions running effortlessly. Let’s go through the step-by-step process of obtaining an apostille for commercial invoices together in this post!
Commercial Invoices in International Business Operations
More than a simple bill, a commercial invoice serves as the primary paperwork in international trade. It not only outlines the financial details of a sale to all stakeholders — including freight carriers and customs agents — but also acts as proof of ownership transfer in compliance with global regulations. Read on for more details.
What Are Commercial Invoices?
Commercial invoices are legally binding documents issued by the seller to the buyer, providing a detailed account of the transaction: the product, value, and contractual terms. Tailored for cross-border movement, they carry crucial information needed for customs clearance, taxation, and payment verification and processing of most international shipments.
Mandatory Data Elements Included in Commercial Invoices
To be considered valid for global trade, commercial invoices must contain specific data. Key elements typically include names and registered addresses of buyer and seller, product descriptions, quantity, unit price, total value, transaction currency, payment conditions, and shipping terms. They must also carry the signature and seal of an authorized company representative to become effective.
Invoice Types and Supporting Documents Used for Apostille or Legalization
Though we’ve established what commercial invoices are in essence, it’s important to note that not every invoice is the same in the eyes of foreign authorities. Depending on the transaction stage, different invoices serve different functions, and preparing the correct document type is essential for authentication.
Commercial Invoice Issued After Shipment
This is the standard finalized invoice created by a seller after the goods are ready for shipment or have been dispatched. The paperwork reflects the definitive, actual transaction, detailing the exact quantities, values, and shipping conditions. Customs rely on post-shipment invoices to calculate duties and taxes, making them the most common type to be submitted for an apostille certification.
Proforma Invoice Used for Pre-Export Transactions
Often issued before shipment or even before production in some cases, a proforma invoice functions as a preliminary, non-binding quote between buyer and seller. It basically provides an estimated price, proposed specifications, and expected terms, often used for securing letters of credit or import permits.
While not carrying legal weight as a final invoice, some countries may accept an apostilled proforma invoice to verify trade intent. Always check with the requesting authority which document they specifically require.
Trade-Related Documents Frequently Submitted Together
Commercial invoices rarely go through the legalization chain alone. They’re often accompanied by supporting documents, such as packing lists, bills of landing, certificates of origin, and insurance policies. Sometimes, corporate paperwork like a certificate of good standing is also required. Submitting them together for authentication reduces the risk of delays and ensures regulatory approval.
Business Scenarios That Trigger Apostille Requirements
Rather than a routine step, an apostille for commercial invoices is a solution triggered by the administrative demands of the receiving country. Particularly, whenever foreign institutions ask for validated invoices, the apostille becomes your hard-and-fast key. Below are some common business situations where it’s needed.
Customs Clearance and Import Compliance
Many customs authorities abroad, especially those with strict import regulations, require authenticated trade documents before goods can legally enter their country. The purpose is to inspect shipment contents and collect taxes in compliance with local laws. The apostille assures customs officials of your invoice’s authenticity, thereby validating the declared product description and value for duty assessment.
International Banking and Payment Verification
Banking and financial institutions often require apostilled commercial invoices to verify international trade deals before they can release funds. This applies to a wide range of bank-mediated payments, such as letters of credit, wire transfers, and financing arrangements. An apostille protects all parties by demonstrating that the invoice is genuine and aligns with the mutually agreed-upon terms.
Contractual and Regulatory Demands from Foreign Authorities
In addition to customs and finance, certain governmental agencies mandate apostilled invoices as part of other trade processes. These may be used for a tender application, import licensing, or product registration with a foreign regulatory body. In such cases, the apostille serves as a fraud prevention measure, enabling your business to meet local legal standards for document authentication.
Sequential Procedure for Apostilling a Commercial Invoice
Apostilling an invoice involves several steps, each of which plays a crucial role in upholding precision and compliance. Although the process can be managed independently, partnering with a reliable apostille service like EZ Apostille for commercial invoices can turn this into a predictable and efficient experience.
Pre-Submission Invoice Validation
Before any official sees your invoice, it must be thoroughly reviewed for accuracy first. Ensure all mandatory data elements, including descriptions, quantities, values, and payment terms, are clear and consistent. The document must also be printed on the company letterhead and free of alterations that could lead to state rejection.
Notarial Certification Stage
Once validated, the invoice will be notarized by a state-commissioned notary public. This critical step confirms the signature of the company representative, building the foundation for the next level of verification at the state office. Thus, notarization is pivotal in the authentication chain and shouldn’t be overlooked.
Government-Level Apostille Processing
The notarized document is then submitted to the Secretary of State or an equivalent state-level authority for apostille certification. This stage typically involves completing a formal request form, paying a processing fee, and submitting the invoice by mail or in-person delivery. Upon approval, an apostille is attached directly to the invoice, proving its legitimacy for use in the destination country.
Completion and Release of Apostilled Documents
Finally, the apostilled commercial invoice is returned to the applicant using the pre-selected method. At this point, carefully check that the certification is properly affixed and all details are correct. The invoice has now become a publicly verified instrument for international trade.
Legalization Pathways for Countries Outside the Hague Convention
When shipping goods to a country outside the Hague Convention, such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, or China, the streamlined apostille process isn’t sufficient for document recognition. Instead, commercial invoices must be processed through a more complex verification chain called legalization.
Chamber of Commerce Authentication
This chain often starts with authentication by a local Chamber of Commerce. The governmental body certifies that the invoice is genuine and issued by a recognized business entity. Their endorsement may take the form of a seal directly placed on the document or a separate certificate of origin, providing commercial credibility.
National Authority Verification
After chamber authentication, the invoice is taken to the U.S. Department of State for national verification. The federal office validates the state official’s signature, confirming that the Chamber’s certification is valid and that it meets U.S. standards for international use.
Embassy or Consular Legalization
The final yet equally crucial step is submission to the consular office of the destination country. Foreign officials will review the previous verifications under that particular nation’s legal framework, then apply their own stamp or seal. This marks the ultimate approval, signaling to the requesting authority back home that it’s safe to use the paperwork within their legal system.
Expected Processing Durations and Cost for Commercial Invoice Apostille
Apostille fees and timelines differ significantly by case, often depending on state agency workload, service options, and shipping methods. Using a standard service may range anywhere between 5 and 15 business days, excluding mailing time. Expedited processing is available in certain areas for an additional fee.
Costs are generally composed of notarial fees, government filing charges, and service provider expenses, if applicable. Clarify directly with the relevant state office or your selected service agent for precise budgeting and timeline planning.
Apostille Considerations for Electronically Generated Invoices
E-invoices are becoming increasingly popular for international trade. However, in most states, the apostille typically requires a verifiable signature on the document for it to be processed. Thus, digital invoices often need to be printed, signed, and notarized before they’re ready to be accepted at the state authority for apostille processing. Always verify specific state requirements to avoid costly refusal.
Professional Apostille Services for Trade Documentation
Relying on professional expertise can be a game-changer when preparing complex trade documents for recognition abroad. Our team provides apostille services for commercial invoices to assist exporters and importers in managing the end-to-end process fast and accurately for uninterrupted global transactions.
Prepared for International Trade
Successfully obtaining an apostille for commercial invoices is a strategic marker for smooth global trade. With the proper steps above and a good understanding of the precise requirements of the receiving country, your goods — as well as their paperwork — will move across borders with both certainty and efficiency.
FAQ
Here are brief answers to some of the most frequent queries we’ve received about commercial invoice apostilles.
Can a commercial invoice be apostilled if shipment details change later?
No, it won’t qualify. An apostille reflects the information included in the invoice at the time of issuance. If shipment details change, the buyer must revise them or create a fresh invoice and complete the apostille process anew.
Is an apostille required for every international shipment or only in specific cases?
An apostille isn’t mandatory for every shipment. It’s often specifically requested by foreign customs, banks, and regulatory agencies for certain goods, values, or procedures. Businesses should confirm the authentication requirements of the importing country before proceeding.
Can multiple commercial invoices be apostilled under a single request?
Yes, they can. You may create a bundle request for multiple documents to the state authority for convenience, but each invoice receives its own apostille certification. Also, note that the exact fees covering the total number of apostilles must be paid at the time of submission.
Does an apostille expire or require renewal for repeated use?
An apostille doesn’t expire, and you don’t need to renew it as long as the information on the underlying invoice remains accurate and unchallenged.
Are handwritten amendments allowed on invoices submitted for apostille?
No, these invoices will be rejected if handwritten amendments are made after the invoices have been signed. They must be clean and typed before submission, as corrections might raise red flags and lead to outright rejection.
Will customs authorities reject goods if the apostilled invoice is delayed?
Delays may cause the importing country to place shipments on hold until proper documentation is presented. This implies financial consequences to the exporter, as demurrage or storage fees are incurred. In some scenarios, authorities even refuse entry entirely, which stresses the importance of timely document authentication.


